Solar energy is being adopted by more and more households and commercial institutions since it is a cleaner, greener, and more affordable alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources. A solar photovoltaic system captures solar energy and converts it into electricity. Transitioning to a solar photovoltaic system can offer the consumer immense cost benefits in the long run. In this article, we will look at all the major components which are a part of any solar photovoltaic system, and uncover the anatomy of a solar PV system.
The following are the most essential components of any solar PV system:
1. Solar PV Panels
Solar panels are the most expensive components of any solar PV system. As a matter of fact, they will make up 60 percent of the cost of the system. It is, therefore, essential that while choosing solar panels, go for the best ones available in the market. Solar panels simply absorb sunlight and convert it into electrical energy. However, at this stage, this electricity is not useful to us – it is a low voltage, DC electricity, and cannot power any appliance in the home or office. It is at this stage that the inverter becomes another essential component of the solar PV system.
2. Solar Array Mounting Racks
There are three ways in which solar panels are mounted: on roofs, on poles, or directly on the ground. Before they are mounted, they are joined in arrays.
The most common form of mounting is roof-mounted solar panels. It is also the most aesthetic and efficient approach. However, roof-mounted systems require high maintenance. For instance, clearing snow or repairing the panels in a high-rise building can be an issue.
Pole-mounted arrays, on the other hand, can be set up at a fixed height which is easier for their maintenance. However, a major drawback of this form of mounting is the additional space that is required for the arrays.
Ground systems are simple to install and cost the least. However, it requires an enormous amount of space to install solar panels on the ground and they cannot be used in areas where there is a regular accumulation of snow.
Irrespective of how and where you mount the arrays, there are two types of mounts – fixed and tracking. Fixed mounts have their angle and height set and they do not move. Tracking arrays on the other hand move east to west to adjust their angle for maximum sunlight reception.
3. Array DC Disconnect/Isolator
Another important component of a solar PV system is the array DC disconnect. It is used for disconnecting the solar arrays from the mains for the purpose of maintenance. It is called a DC disconnect because the solar panel generates only DC current before the inverter converts it into AC.
The DC isolator is a manually operated switch. It aids in the quick shutdown of electricity transmission from the panels to the inverter in emergency situations.
4. AC Isolator
AC isolators work on the same principle as the DC isolator, but in this case, the system can be shut down by disconnecting it from your home. This is done during emergencies. However, remember that there is a specific shutdown procedure that needs to be followed while disconnecting. Follow the instructions carefully, and hire a qualified solar installer to conduct any kind of maintenance work.
5. Inverter
This is the second most expensive component of a solar PV module after solar panels. Since standard home appliances run on AC current, the low, DC current generated by the solar panels cannot be used. It is the inverter that converts the DC current generated by the solar panels and the batteries to the AC current used by the appliances. The inverter boosts the current-voltage to 240V AC, which is suitable for all home appliances.
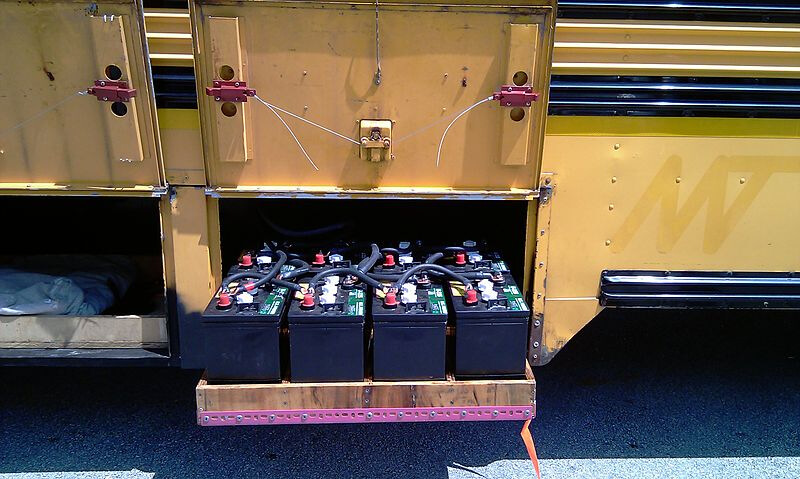
6. Battery Pack
A solar PV system entirely depends on sunlight for generating electricity. However, sunlight is available only during the daytime. Besides, during rainy/cloudy days, the duration of sunlight reception diminishes. Therefore, a solar PV system comes with batteries, which can store the energy produced during the daytime and can be used to power appliances throughout the day.
7. Consumption meter
The consumption meter is an optional device, which enables you to monitor the energy consumed by the household and the energy generated by the solar PV system. It also helps you determine the amount of money you are saving on your energy bills due to the use of solar energy in real-time. Besides, it helps you know when you can shift the use of certain appliances to particular times during the day, when energy generation is maximum.
8. Power meter
Solar energy, in most instances, is not always sufficient to power all the appliances in your household throughout the year. There are seasons when the sunlight reception is not enough to generate electricity to power the house. Therefore, there must be an alternative connection in place to the main electricity grid of your locality. A power meter measures the amount of power used from the grid. In solar PV systems which use net metering, the power meter is bidirectional, i.e. it measures the amount of power the solar system sends back to the grid.
9. Backup Generator
Solar PV systems which are not tied to the power grid make use of a backup generator to power the house during periods of low power output. If you are concerned about the environmental impact of generators, you can install a generator that runs on alternative, cleaner fuels such as biodiesel, rather than diesel or kerosene.
10. Breaker Panel and Circuit Breaker Panel
The breaker panel is the point to which the power source is joined to the electrical circuits of your house. A circuit consists of a continuous route of wire that connects outlets and lights in an electrical system. There exists a circuit breaker for each circuit, which prevents the appliances on a circuit against overloading and causing a fire hazard. In the event of an overload, the circuit breaker will switch off, thus, interrupting the flow of electricity.
11. Charge Controller
The charge controller maintains the proper charging voltage for the batteries of a solar PV system. Continuous voltage can lead to an overcharging of the batteries. By regulating voltage, the charge controller prevents overcharging and allows charging only when required.
12. The main fuse box (switchboard)
In general, if you are not using an old or a tiny fuse box, you can make use of your existing fuse box for the newly installed solar PV system. However, your new system will be wired into your existing fuse box, so that it can supply electricity to the house wiring, grid, and meter.
Conclusion
Thus, in this article, we listed down all the essential components of a solar PV system, uncovering the anatomy of a solar PV system. Solar energy is a clean and green alternative to conventional fossil fuel-based energy solutions. It is a futuristic energy solution and must be adopted on a larger scale to mitigate the effects of climate change.
- 300 Watt Solar Panel Prices in India: 2023 - March 8, 2023
- 500 Watt Solar Panel Prices in India: 2023 - March 5, 2023
- Loom Solar Panel Price: 2023 - February 19, 2023